The act of
evaluating and
comparing the
identified groups
and then selecting
one or more of
them as the
prospects
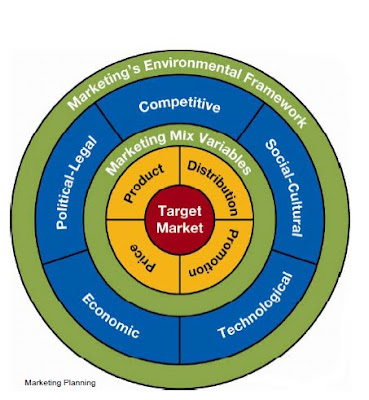
marketing ,Business Orientations to the marketplace,Marketing MIX ,marketing research ,Business Practices ,Research Approaches,Sampling Plan,SWOT Analysis,Marketing Plan Outline ,marketing management and brand name
Once the market potential has been estimated, you
have to determine how much of that market you can
obtain (what “market share” can you capture.
Then you develop specific marketing strategy for the
You create a “Forecast” of the market potential within
each segment.
This is the “go, no-go” stage. When you are at this
stage you gather the information on sales potential
to determine whether you can go further ahead and
justify further analysis. And we must say that
Forecast - “what if” - an expectation of future
Action.
Once the segments have been identified you should develop a profile of the relevant customer
needs and behaviors in each segment. You must answers some question such as :
What does your customer look like (profile)!!?
What do they like!!?
What do they do!!?
- You need this description to be very precise in
order to make your marketing “match” the needs
of the customer

This process starts when a company looks at the
Potential customers and identifies those
customers as having particular characteristics -
these characteristics will allow the marketing
Company to classify them into market segments.
After collecting the data the researcher will tabulate the data & apply
Statistical methods & techniques
STEP FIVE:
Present the findings
The researcher should not overwhelm management with figures & statistical
Techniques but rather should present major findings that are relevant to the
Major marketing decisions facing management
The third step in Marketing Research Process
Collect the information
The most expensive & the most prone to error:
- Some respondents will refuse to co-operate
- Some respondents will give biased answers
- Some interviewers will be biased & dishonest
How the Subject should be contacted, The choices are:
1- Mail Questionnaire: it is the Best way to reach people who would not give personal interviews or could be biased or distorted
By interviews
Telephone Interviewing:
It Is the Best method for gathering information quickly, but it has to be short & not too personal
Personal Interviewing:
Most expensive – additional observations – it is
Subject to interviewers bias or distortion
This plan calls for three decisions:
Sampling Unit “Who is to be surveyed “
Defining the Target population that will be sampled, where the sampling frame
Must be developed so that everyone in the population has an equal chance of
Being sampled
Sample Size how many people should be surveyed?
Larger samples are more reliable, however samples less than 1% of the
Population can give good reliability
Sampling Procedure
How should the respondents be chosen?

1-Questionnaires: Consists of a set of questions presented to respondents for
Their answers, it the most common instrument used for
Collecting primary data for its flexibility
But for successful Questionnaires It Should be:
1- Carefully developed & debugged before administrated on a large scale
2- Carefully choosing questions wording & sequence
3 - Avoid repeated & boring questions - Choose simple and direct unbiased questions
4- Logical Order
Carefully choosing questions’ form
-Close-end questions: Have specific answers. (e।g।: Answered by Yes/No)
Open-end questions: Free to express thoughts. (How Interviewee thinks & Feel ,……etc
There are many steps but shortly ill talk about it
�� Step 1: Define the Problem, the
Decision Alternatives and the Research
Objectives
�� Step 2: Develop the
Research Plan
�� Data Sources (primary, secondary)
�� Research Approaches
�� Observational research
�� Focus group research
�� Survey research
�� Experimental research; Behavioral data
![]()

Firstly we must know the the difference between:
Production concept: assumes consumers favor
those products that are widely available and
affordable. (Focus: wide distribution; high
volume).
2. Product concept: assumes consumers will favor
those products that offer the most quality,
performance, and features.
3.Selling concept: assumes that consumers will
either not buy or not but enough of the
organizations’ products unless the organization
makes a substantial effort to stimulate the
customer’s interest in the product. (Focus:
needs of the seller)
4.Marketing concept: holds that the key to
achieving organizational goals consists in
determining the needs and wants of target
markets and delivering the desired satisfactions
more effectively and efficiently than
competitors. (Focus: different needs of buyers)
5. Societal marketing concept: [adds to the
marketing concept the words] … for the
objective of preserving and enhancing the
consumer’s and society’s well being. (Focus:
needs of buyers and society)
The development of definitions of marketing
MARKETING is the performance of business activities
that direct the flow of goods and services from
producers to consumers. (The 1935 Definition)
MARKETING is the process of planning and executing
the conception, pricing, promotion and distribution of
ideas, goods and services to create exchanges that
satisfy individual and organization objectives. (The 1985 Definition)
MARKETING is an organizational function and a set of
processes for creating, communicating and delivering
value to customers and for managing customer
relationships in ways that benefit the organization and
its stakeholders.
(The 2000 Definition)
But finally thanks to Mr. Ramy Khodeir and his teamthey help me to prepare this study